News
EALA approves 2013/14 Annual Report of the Community

EALA on 3 February 2016 debated and approved the EAC Annual Report 2013/14. The Assembly, meanwhile, urged the Council of Ministers to ensure further improvements in future subsequent reports and in all EAC documents by enhancing overall supervision and quality control. This measure is geared towards sustaining high standards in all outputs of the Community.
The debate was preceded by tabling and debate of the Report of the Committee on General Purpose (GPC) on the EAC Annual Report for 2013/2014. The report of the GPC followed the consideration of the Annual Report for the year 2013/14. The Committee Report presented by the Chairperson of the Committee on General Purpose, Hon. Dr Odette Nyiramilimo urges the Council of Ministers to make follow up on actions with intention to amend, retract or correct identified parts of the Annual Report that may be erroneous.
The Committee on General Purpose further calls for additional details to be included on the status of major Community Projects such as those under Infrastructure Sector. The details should, inter-alia, include updates on status, causes for delay and other challenges realised under the Road network, Railway sector and the EAC Master Plan.
The Committee also observes that the EAC Annual Report 2013/14 contains no section on challenges either than what is mentioned by the Deputy Secretary-General of the EAC in his submission to the Committee.
“As it has been noted in previous reports tabled before the House, there is apparent hesitation to clearly point out challenges in the EAC Annual Report,” Hon. Odette Nyiramilimo noted. Each year, the Chairperson of the Council of Ministers submits an Annual Report on the activities and achievements of the Community to key stakeholders in line with Article 49(2)(c) of the Treaty.
The Annual Report illustrates the accomplishments of the various Organs and Institutions of the Community within their respective mandates and missions. The 2013/4 Report captures the progress made in implementation of various activities including the Protocol on establishment of the East African Monetary Union, operationalisation of the single Customs Territory, Infrastructure development, productive and social sectors and the progress on the internationalisation of the new generation EAC e-Passport.
At debate, Members called on the Council of Ministers to cause for take up more shares in East African Development Bank (EADB).
Hon. Shyrose Bhanji supported the move for Partner States to take more shares in the EADB.
“It is shocking to hear that our partner States have minority shareholding in the Bank. We are supposed to take advantage of the bank. What is the problem? We cannot be seen to transform agriculture which is our backbone through donor funding,” she added.
Hon. Dora Byamukama supported the adoption of the Annual Report but said it was necessary for the Assembly to debate on documents that are current. Others who supported the report were Hon. Christophe Bazivamo, Hon. Nancy Abisai, Hon. Bernard Mulengani, Hon. Straton Ndikuryayo and Hon. Valerie Nyirahabineza.
The Chairperson of the Council of Ministers, Hon. Dr Susan Kolimba affirmed that the Council would make every effort to enhance the quality of its Annual Reports.
East African Community Annual Report 2013/14
Chapter 7. Office of the Director General – Customs and Trade
The Office of the Director General (Customs and Trade) is responsible for the implementation of the customs and trade (internal and external) functions in the EAC. Customs encompasses tariff and valuation, compliance and enforcement, procedures and facilitation while trade covers international trade, internal trade and Standards, Quality Assurance, Metrology and Testing.
Customs
Implementation of the EAC Single Customs Territory: Following the decision of the Summit in April 2012 to adopt the destination principle for the implementation of the EAC Single Customs Territory and commence the implementation on 1st January 2014, the Council in November 2013 approved a Framework and roadmap for its implementation.
In order to implement the directives, the Committee on Customs constituted five Technical Working Groups (TWGs), namely: Business Flows and Legal; ICT; Compliance and Enforcement; Capacity Building and Change Management; and Inter-Agency Cooperation to develop the required instruments for operationalization of the EAC Single Customs Territory. The Committee undertook a number of activities and developed the operational instruments including: the SCT business process manual; Compliance and Enforcement Framework; and proposed amendments to the EAC Customs Management Act and regulations to cater for the SCT. Activities undertaken during the period under review included developing capacity building and change management intervention tools to support the implementation of the SCT.
Enhanced Trade Facilitation and Customs Services through Interconnectivity of Customs Systems: Following the finalization of the Study on the Interconnectivity of customs systems, the Council directed the Secretariat to develop Customs Information Technology regulations to reinforce the use of IT in Customs. As at 30th June 2014, the draft regulations were awaiting final adoption by Council after legal input by the Sectoral Council on Legal and Judicial Affairs.
Review of Rules of Origin: The draft revised EAC Rules of Origin were considered by the Sectoral Council on Trade, Industry, Finance and Investment during its meeting in May 2013 that among others, directed that further consultations and sensitization of stakeholders be undertaken. The Secretariat undertook the consultations in the Partner States particularly on the following new elements:
(a) Simplification of origin criteria:
-
Value added criterion by proposing to lower the threshold from 35% to 30% and using the Ex-works price instead of Ex-factory costs;
-
Change in Tariff Heading has been made more flexible to some goods by allowing changes in Tariff Sub-headings;
-
Introduction of specific manufacturing processes as a qualifying criterion to some goods, such as manufacturing to start from completely knocked down kits for motor vehicles assembled in the region.
(b) Review of the definition of ownership of a fishing vessel of a Partner State by lowering the threshold of ownership from 75% to 20%;
(c) Introduction of a rule that provides for the treatment of goods sold in sets;
(d) Establishment of central database of registered exporters at the Secretariat;
(e) Provision for other forms of cumulation other than full cumulation such as cumulation with countries or Regional Economic Communities that EAC has concluded a Free Trade Area with;
(f) Introduction of a rule on Approved Exporter, where the competent authorities of the exporting Partner States may authorize any exporter who makes frequent shipments of products;
(g) Introduction of a rule on validity of proof of origin where proof of origin shall be valid for six months from the date of issue in the exporting country.
Development and Review of Customs Laws and Regulations: Work towards amending the EAC Customs Management Act commenced in order to align it with the procedures under the Framework of the Single Customs Territory. The 27th Meeting of the Council held in August 2013 approved the recommendations to amend certain provisions of the EAC Customs Management Act and EAC Customs Management Regulations and referred the provisions to the Sectoral Council on Legal and Judicial Affairs for legal input.
Establishment of One Stop Border Posts (OSBP): There were fifteen OSBP Projects at various levels of development on internal borders in the region supported by various Development Partners. Construction at Taveta, Namanga, Rusumo, Isabania, and LungaLunga/ Hororo were at advanced stages of completion while work on Kabanga, Busia, Mutukula, Malaba, Katuna, Kagitumba/Mirama Hills was expected to progress faster given that most contractual issues had been resolved. One stop border posts infrastructure at Holili, Sirari,Nemba/Gasenyi and Ruhwa had been completed while construction at Tunduma and Kobero was planned to commence late in 2014.
Capacity Building in Customs: The EAC Customs Training curriculum was rolled-out in November 2012 in Rwanda and officially launched in May 2013 by the Committee on Customs. The other four Partner States commenced implementation in July 2013. The EAC Customs capacity building initiatives focused on developing tools to support the implementation of the EAC Customs training curriculum. The training materials were published and distributed to Partner States for application.
Regional Time Release Study: The East African Community (EAC) in conjunction with the World Customs Organization (WCO) conducted a Regional Time Release Study (TRS) on the Central Corridor between Dar es Salaam and Bujumbura and Kigali via Kabanga/Kobero and Rusumo borders respectively. The Study which commenced in February 2014 developed terms of references, work plan, questionnaires, and a budget. The TRS experts also undertook a route survey and sensitization of the stakeholders that was slated for completion by end of September 2014.
Customs Integrity Action Plan: The Secretariat in collaboration with customs experts from revenue authorities developed and finalized the EAC Customs and Tax Integrity Action Plan and the Regional Code of Conduct in July 2013. The document was submitted to the Partner States for further consultations.
Duty Remission for Motor vehicle Assemblers: The Sectoral Council on Trade, Industry, Finance and Investment at its meeting held on 10th June 2013 in Arusha, considered the recommendations of the Committee on Customs to adopt the list of items to be excluded from CKD for vehicle assemblers, items to be included in the CKD kits for assembling of trailers and the level of breakdown of CKD kits for motor vehicles. SCTIFI directed the Secretariat to conduct a comprehensive regional study and finalise the regulations. The Secretariat coordinated the validation and finalized the regulations which are awaiting consideration by SCTIFI.
Trade
The EAC Mechanism on Elimination of Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs): The EAC Time Bound Programme (TBP) on elimination of Non-Tariff Barriers was updated during the 14th Regional Forum on NTBs held in February 2014. Seven (7) new NTBs were reported by the Partner States.
Development of a Legally Binding Mechanism on Elimination of NTBs: The draft EAC NTBs Bill was adopted by the Council in November, 2013 and forwarded to the Sectoral Council on Legal and Judicial Affairs for legal input. Once the Bill is enacted into law, it will enhance the work of EAC Regional Forum on NTBs and the National Monitoring Committees on the elimination of NTBs as contained in the EAC Time-bound Programme.
Compilation and Dissemination of Trade Statistics: As a strategy to improve both internal and external trade, the Community annually compiles and publishes the Trade Report highlighting EAC intra-trade and Customs revenue and investment performance in the Community, among others. The EAC Trade Report 2012 was finalized and printed. Preparation of the zero draft of the EAC Trade report 2013 was on-going.
Promotion of Jua Kali/NguvuKazi Artisans: The Jua Kali/NguvuKazi Artisans Exhibitions have been held annually in the Partner States on rotational basis since 1999. The main objective of the annual Exhibition is to facilitate the formalization of informal sector activities within the East African region by allowing the artisans to meet, exchange business information, and expand markets for their products in order to exploit opportunities offered under the EAC Common Market. The specific objectives are to bridge the gaps in trade, culture and social economic imbalances in the region; create awareness of the sector’s potential in producing and providing affordable goods; create expanded investment opportunities for the region’s up-coming/emerging entrepreneurs; and initiate dialogue between the entrepreneurs and sharing knowledge in technology, innovations and business techniques.
The 14th EAC JuaKali/NguvuKazi Exhibition was held in Nairobi, Kenya in December, 2013 and the Post exhibition Report was prepared with key recommendations and lessons for improvement of future exhibitions. A total of 500 artisans drawn from the Partner States were sensitized on market opportunities in the EAC.
Trade in Services Under the EAC Common Market Protocol: In June 2013, the Sectoral Council on Trade, Industry, Finance and Investment (SCTIFI) directed Partner States to make proposals in accordance with Article 53 of the Common Market Protocol (CMP), for amendment of the relevant Articles of the EAC CMP that affect trade in services and free movement of workers by February 2014. The directive was based on the fact that Partner States were of the view that it was difficult to implement Trade in Services provisions in the CMP and the schedules of commitments due to some technical errors, omissions and legal inconsistencies/discrepancies. A meeting of Experts on trade in services held in April 2014 developed proposals for amendment of the relevant Articles on Trade in Services and free movement of workers under the EAC CMP, which were subsequently adopted by the SCTIFI meeting held in May 2014.
Further, under the World Trade Organisation (WTO) Transparency Mechanism, the WTO Secretariat prepared a Factual Report on the Provisions on Trade in Services under the EAC CMP. EAC meetings of Experts on Trade in Services were held in January and May 2014 to develop comments on the Report and responses to the questions raised by Colombia, Chile and Canada. The Factual Report was adopted by the 73rd WTO Transparency Session of the Committee on Regional Trade Agreement held in June 2014 in Geneva, Switzerland.
Finalization and Implementation External Trade Agreements: During the reporting period, the Community continued to negotiate external trade agreements namely, the EAC-EU Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) and the EAC-U.S. Trade and Investment Partnership (TIP).
Under the EAC-EU EPA Negotiations, substantial progress was made on the issues under the negotiations. As of March 2014, both Parties had reached agreement on the outstanding issues under Institutional Arrangements, Dispute Settlement, Rules of Origin and Most Favored Nation Clause. Outstanding issues remained on Export Taxes, Agricultural Domestic Support, Relations with the Cotonou Agreement, Good Governance on Tax Matters and Consequences from Customs Union Agreements concluded with the EU.
Regarding the EAC-U.S. TIP, the first public-private sector EAC-U.S. Commercial Dialogue was held in August 2013. The EAC and U.S. private sectors jointly enumerated priority areas including trade facilitation and related infrastructure, energy, agribusiness, services, access to finance and markets, development of supply chains and strengthening of women in business leadership. Subsequently, exploratory discussions were held between the EAC-U.S. Technical Officials Meeting in February 2014 in Bujumbura, Burundi to discuss the components of the TIP, namely Regional Investment Treaty, Trade Facilitation Agreement, Trade Capacity Building Assistance, SPS and TBT; and Commercial Dialogue. Both parties agreed on follow up actions.
Model Investment Treaty: The Secretariat developed a draft Model Investment Treaty to be used by the EAC Partner States as a basis for negotiations with third parties. The draft was submitted to Partner States for further consultations.
Finalization of EAC Joint Export and Investment Promotion Strategy 2013-2017: The EAC Export Promotion Strategy 2013 - 2017 was considered by the Council in June 2013. The key highlight of the EAC Export Promotion Strategy was the separation of the joint EAC Export and Investment Promotion Strategy.
Development of Efficient Export Incentives: The development of policies for the Export Processing Zones (EPZs) and the Special Economic Zones (SEZs) continued during the reporting period. The SEZs Policy and the draft study report on the impact of the Customs Union on the existing EPZs/SEZs firms were reviewed and validated respectively.
Implementation of EAC SQMT Act 2006: During the period under review, thirty eight (38) Standards were developed and approved by East African Standards Committee, and were awaiting adoption by Council. In addition, three (3) sets of regulations to operationalize the SQMT Act were adopted by the Council in November 2013. As part of the follow-up on the implementation of harmonized standards at the regional entry points, a monitoring mission was undertaken to eight (8) border posts in the region.
Negotiations for the Establishment of the COMESA-EAC-SADC Tripartite Free Trade Area: The Tripartite Trade Negotiation Forum (TTNF) established four (4) Technical Working Groups (TWGs): Customs Cooperation; Rules of Origin; TBT/SPS/NTBs; and Trade Remedies and Dispute Settlement. The TWGs concluded the situational analysis on key thematic issues for substantive negotiations and considered the respective annexes (3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9 and 10) of the draft FTA Agreement. The TTNF also commenced text-based negotiations schedule and adopted Annex 6 of the draft TFTA Agreement on Simplification and Harmonization of Trade documentation and procedures. More critically, the TTNF resolved the contentious issues on modalities for tariff liberalization which cleared the way for Tripartite Member/Partner States to embark on preparation and exchange of their tariff offers.
On negotiations on movement of business persons, the Tripartite Task Force (TTF) Chief Executive Officers established a TTF Sub Committee on Movement of Business Persons (SCMBP). The TTF SCMBP held its inaugural meeting in April 2013 in Nairobi Kenya and reviewed the draft terms of reference (ToRs) for the proposed Tripartite Technical Committee on Movement of Business Persons (TTC-MBP); updated the draft Situational Analysis of the Movement of Business Persons in the three RECs; and prepared a work programme on negotiations on movement of business persons.
Under the Tripartite industrial development pillar, a Tripartite Regional Consultative Workshop was held in June 2013, in Nairobi, Kenya. The workshop brought together stakeholders from ministries of trade and industry in the Tripartite region as well as the private sector and enabled them to provide inputs to the draft Work Programme/Roadmap on the Tripartite Industrial Development Pillar.
Under the Tripartite infrastructure development pillar, work progressed on Operationalisation of the Joint Competition Authority (JCA); Tripartite Corridors Infrastructure Development and Border Posts and development of a Tripartite Infrastructure Master Plan (including Development of the Project Database and Tripartite Work on Corridor Monitoring).
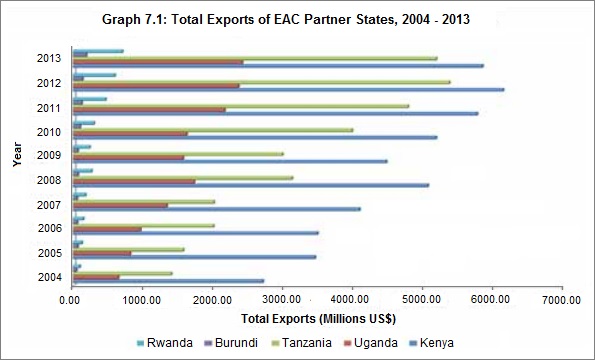
Exports: The value of total exports by the EAC Partner States has more than tripled from USD 4.9 billion in 2004 to USD 14.3 billion in 2013 with respective shares of 41% (Kenya), 36% (Tanzania), 17% (Uganda), 5% (Rwanda) and 1% (Burundi). Graph 7.1 shows the upward trend in the value of exports, with Kenya as the lead exporting country, followed by Tanzania, while Burundi has the least exports in value terms.
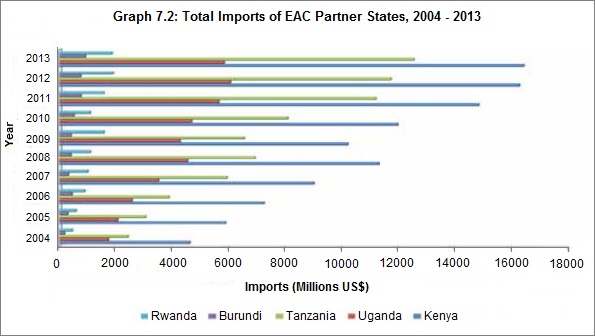
Imports: The value of total imports by the EAC Partner States has more than quadrupled from USD 9.4 billion in 2004 to USD 37.5 billion in 2013 with respective shares of 44% (Kenya), 33% (Tanzania), 16% (Uganda), 5% (Rwanda) and 2% (Burundi). Graph 7.2 shows the trend in the value of imports, with Kenya as the lead importing country, followed by Tanzania, while Burundi has the least imports in value terms.
Intra-EAC Exports: The value of intra-EAC exports by the EAC Partner States has increased from USD 3.1 billion in 2004 to USD 5.6 billion in 2013. Graph 7.3 shows the upward trend in the value of intra-EAC exports, with Kenya as the lead exporting country, followed by Tanzania, while Burundi has the least exports in value terms.
Intra-EAC Imports: The value of intra-EAC imports by the EAC Partner States increased from USD 0.7 billion in 2004 to USD 2.1 billion in 2013 with respective shares of 16% (Kenya), 19% (Tanzania), 30% (Uganda), 19% (Rwanda) and 16% (Burundi). Graph 7.4 shows the trend in the value of intra-EAC imports, with Uganda as the lead importing country, followed by Tanzania, while Burundi and Kenya were the least importers in value terms.




