Blog
SACU trade 2019

The Southern African Customs Union (SACU), comprising Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia and South Africa, is a customs union (CU) with duty-free[1] intra-SACU trade and a common external tariff (CET) applicable to all imports from outside the region. SACU members are also members of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) free trade area (FTA). Eswatini is a member of the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA), and has preferential access to some COMESA countries under derogation yet is exempt from reciprocating preferences due to its membership of SACU.
In terms of Article 31 of the SACU Agreement, SACU member states will establish a common negotiating mechanism to negotiate trade agreements with third parties as a bloc. This is to ensure that the integrity of the customs union and its common external tariff are protected. SACU has concluded preferential trade agreements with the Common Market of the South (MERCOSUR),[2] and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).[3] SACU is also participating in the Tripartite Free Trade Area (TFTA) negotiations; and has already concluded negotiations for tariff concessions with the member states of the East African Community (EAC). Negotiations with India to conclude a preferential trade agreement (with limited tariff liberalisation) has also been ongoing for a number of years.
SACU members, along with Mozambique, have concluded an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) with the European Union (EU)- SADC EPA.[4] The UK and SACU members and Mozambique have signed an EPA, which will govern their trade and economic relations post-Brexit.
In this Blog we analyse SACU’s trade in 2019 (available data): intra-SACU trade, SACU trade with the rest of Africa, EAC, the EU and the UK.
Intra-SACU trade
In 2019, intra-SACU trade was 14% of world trade. Intra-SACU exports amounted to US$14.42 billion (49% of intra-Africa exports, and 4% of SACU’s world exports). Intra-SACU imports accounted for 62 per cent of SACU’s imports from Africa, and 13% of world imports. Products mainly traded within SACU include mineral fuels and oils, precious stones, vehicles, general machinery, electrical machinery and equipment, perfumes, cosmetics or toiletries, sugar and sugar confectioneries, beverages, spirits and vinegar.
In 2019, Botswana imported 31 per cent of intra-SACU imports, followed by Namibia (27%), South Africa (24%), Eswatini (10%), and Lesotho (8%). South Africa was the largest intra-SACU source market, exporting 73 per cent of intra-SACU exports. Namibia and Eswatini exported 10 per cent each, Botswana 5 per cent and Lesotho 2 per cent.
African countries outside SACU
In 2019, SACU exports to African countries outside SACU were valued at approximately US$15 billion (51% of SACU’s African exports). SACU’s main trading partners in Africa are SADC member states; Nigeria, Ghana and Kenya are also important partners. All SADC member states – except Angola, DRC and Comoros – are in an FTA.
Top products exported by SACU to other African countries include chromium oils, light oils, goods vehicles, non-agglomerated iron ore, electrical energy and bituminous coal. Mozambique was the largest destination market, importing 25 per cent of SACU’s exports to other African countries. Zambia imported 16 per cent and Zimbabwe 14 per cent. To Mozambique, SACU mainly exported ores, slag and ash; mineral fuels and oils; general machinery and iron and steel; to Zambia, frozen mackerel, goods vehicles and sulphur; and to Zimbabwe, light oils, goods vehicles and electrical energy. Trade between SACU countries and Mozambique, Zambia and Zimbabwe is under the SADC Protocol on Trade – i.e. SADC FTA preferential tariffs are applicable.
SACU imports from other African countries amounted to US$8.5 billion (38% of African imports, and 8% of world imports). From this region, SACU imported mainly crude petroleum oil, copper (unrefined & refined), electrical energy, and natural gas. These products were imported duty-free into SACU.
Nigeria was the biggest African source market outside SACU (accounting for 41% of SACU’s imports from Africa), followed by Zambia (18%), Mozambique (11%), Ghana and Angola (7% each). From Nigeria, SACU mainly sourced crude petroleum oils, urea and natural rubber; from Zambia, copper and electrical energy; from Mozambique, natural gas, electrical energy, light oils and bituminous coal; from Ghana, crude petroleum oil and cocoa paste; and from Angola, crude petroleum oils and non-industrial diamonds.
Nigeria’s crude petroleum oils, urea and natural rubber were imported duty-free into SACU. Zambia’s copper and electrical energy and Mozambique’s natural gas, electrical energy, light oils imported duty-free into SACU (i.e. under the SADC FTA preferential tariffs). Ghana’s crude petroleum oil and cocoa paste as well as Angola’s crude petroleum oils and non-industrial diamonds were imported duty-free into SACU; the applicable rates being the MFN duties.
SACU-EAC trade
All SACU and all EAC Member States (except Tanzania) trade under MFN rates of duty. SACU Member States trade with Tanzania under the SADC FTA, and will continue to do so when trade under the AfCFTA begins. In 2019, SACU imports from and exports to EAC were worth about US$64 million (0.3% of African imports), and US$1.62 billion (6% of African exports), respectively. Top products imported by SACU from EAC include coffee, cotton t-shirts, unused postage, black fermented tea, cigarettes, unmanufactured tobacco, and fresh-cut roses. Products mainly exported by SACU to EAC were flat-rolled iron/steel products, mixtures of odoriferous substances (additives used in the food and beverage industry), goods vehicles, hot-rolled bars and rods and bituminous coal.
EAC’s coffee, medicaments, unrooted cuttings and slips and unmanufactured tobacco were imported duty-free into SACU. Cotton t-shirts and cigarettes were levied a 45 per cent duty. Fresh-cut roses faced a 20 per cent duty. Black fermented tea was levied a specific tariff of 400c/kg. Unused postage was imported duty-free or at 15 per cent duty (depending on the tariff line).
Half of SACU’s imports from EAC were sourced from Tanzania, 34 per cent from Kenya, 12 per cent from Uganda, 3 per cent from Rwanda and 1 per cent from Burundi. 56 per cent of SACU’s exports to EAC were destined for Kenya, 32 per cent for Tanzania, 10 per cent for Uganda and 2 per cent from Rwanda.
SACU-EU trade
SACU’s imports from and exports to the EU amounted to US27.8 billion (26% of world imports), and US$24.9 billion (24% of world exports), respectively. The main products sourced from the EU by the SACU countries include commodities not elsewhere specified, unused postage, medicaments and passenger vehicles. EU’s unused postage and medicaments are imported duty-free into SACU, passenger vehicles are imported duty-free or at 18 per cent duty – depending on the tariff line. All of SACU’s imports of fuel elements cartridges, wire catalysts, light vessels, corks and stoppers, rhodium, steel alloy, retreaded pneumatic rubber tyres, unwrought chromium and sugar beet seed were sourced from the EU.
Germany was SACU’s biggest EU source market, accounting for 32 per cent of SACU’s imports from the EU. The UK exported 11 per cent, Italy 9 per cent, France 8 per cent, and Spain 6 per cent. Netherlands, Belgium, Sweden and Poland 4 per cent each.
South Africa imported 94 per cent of SACU’s imports from the EU, Namibia imported 3 percent, Botswana 2 per cent, Eswatini 0.3 per cent and Lesotho 0.1 percent.
The main products exported by SACU to the EU include passengers and goods, platinum (semi-manufactured), diamonds, iron ores, copper and fresh grapes. Most of the SACU’s exports to the EU were destined for Germany (31%), UK (19%), Belgium (18%), Netherlands (12%), Spain (6%) and Italy (4%).
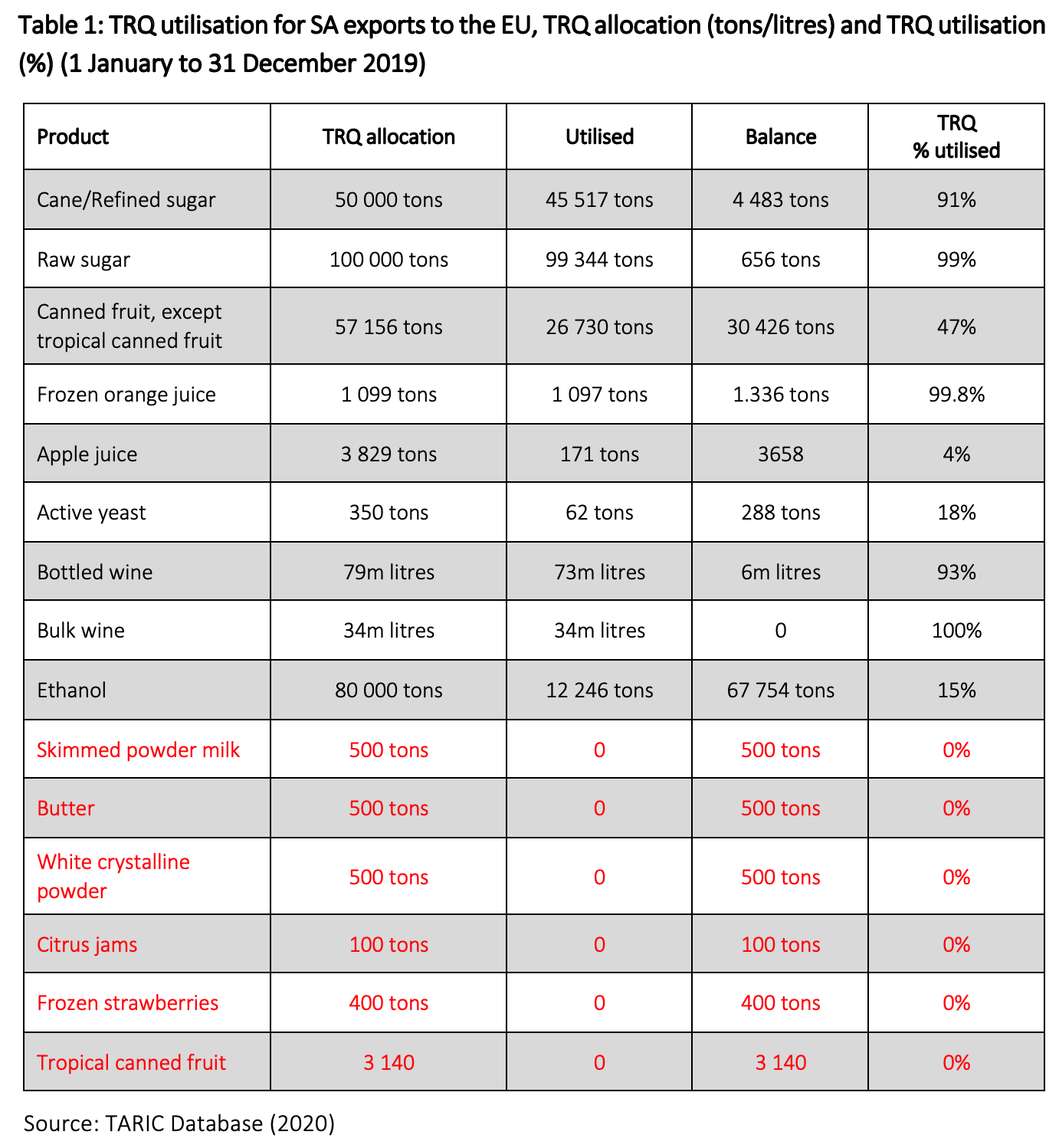
Under the SADC EPA, Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia and Mozambique have duty-free quota-free access into the EU. South Africa is also granted duty-free access for certain goods (fresh flowers) as well as some tariff rate quotas (TRQ) into the EU – i.e. South Africa’s exports to the EU within the quota are charged lower tariffs than exports outside of the quota. Table 1 shows that, in 2019, South Africa only exhausted the TRQ for bulk wine. Usage of TRQs for processed dairy products[5], fruit products, and white crystalline powder was zero.
SACU-UK trade
In 2019, SACU’s imports from and exports to the UK were valued at US$3 billion and US$4.8 billion, respectively. SACU’s imports from the UK accounted for 11 per cent of SACU’s imports from the EU, and exports accounts for 19 per cent of SACU exports to the EU. From the UK, SACU mainly imported unused postage (28% of SACU’s imports from the UK), original motor vehicle component parts (5%), whiskies (5%), passenger vehicles, dumpers, medicaments and processing units for automatic data-processing machine (2% each).
UK’s unused postage, whiskies, medicaments and processing units for automatic data-processing machine are imported duty-free into SACU. Dumpers were imported at 5 per cent duty, passenger vehicles duty-free or at 18 per cent duty, depending on the tariff line.
All of SACU’s imports of, photographic film in rolls, amino resins, piperidine and pigs’ bristles were imported from the UK. These products were imported duty-free into SACU.
Top products exported to the UK by SACU were platinum (33% of SACU’s imports to the UK), goods and passenger vehicles (20%), rhodium (5%), palladium (4%) and fresh grapes (3%). All of SACU’s exports of molybdenum waste and scrap, woven fabrics (HS521141; HS551513), circuses and silver base metals clad are destined for the UK.
[1] The only exception is additional duties which can be levied in the protection of an infant industry. Both Botswana and Namibia have levied these additional duties and currently Botswana as an additional duty of 40 per cent applicable to the importation of certain UHT milk. The duty is applicable to all imports – from outside and inside the common customs area.
[2] MERCUSOR members include Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. The SACU-MERCUSOR Preferential Trade Agreement entered into force on 1 April 2016.
[3] EFTA members include Iceland, Liechtenstein and the Swiss Confederation. The SACU-EFTA Free Trade Agreement entered into force on 1 May 2008.
[4] SADC EPA has been provisionally implemented since 10 October 2016.
[5] South Africa currently does not comply with the sanitary and phytosanitary requirements to export certain products, like milk and strawberries to the EU. Accordingly, they are unable to take advantage of the tariff rate quotas in place.
About the Author(s)
Leave a comment
The Trade Law Centre (tralac) encourages relevant, topic-related discussion and intelligent debate. By posting comments on our website, you’ll be contributing to ongoing conversations about important trade-related issues for African countries. Before submitting your comment, please take note of our comments policy.
Read more...




