News
Seven essential guiding principles to boost financial inclusion laid out in new report

Seven guiding principles to help countries increase financial inclusion were set out in a report released on 5 April 2016 by the Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures (CPMI) and the World Bank Group.
The Payment aspects of financial inclusion report builds on a document that underwent public consultation in late 2015 and seeks to tackle barriers to the adoption and usage of transaction accounts, which sit at the heart of retail payment services.
A transaction account is an essential financial service that can serve as a gateway to other financial services such as savings, credit and insurance. However, nearly 40% of the world’s adult population – about 2 billion people – still have no account with a bank or authorised non-bank servicer provider.
In addition to outlining principles to help countries advance financial inclusion, the report suggests possible key actions, including providing basic accounts at little or no cost, stepping up efforts to increase financial literacy, and leveraging large-volume payment programmes, such as government payments, by adopting electronic payment services. Financial inclusion efforts are beneficial not only for those who will become financially included, but also for the national payments infrastructure and, ultimately, the economy.
These guiding principles are:
-
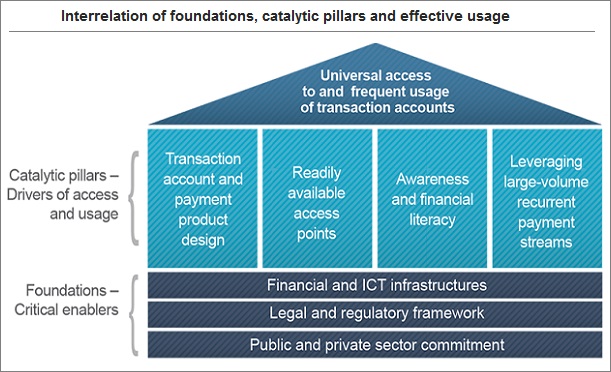
Guiding principle 1: Public and private sector commitment: Commitment from public and private sector organizations to broaden financial inclusion is explicit, strong and sustained over time.
-
Guiding principle 2: Legal and regulatory framework: The legal and regulatory framework underpins financial inclusion by effectively addressing all relevant risks and by protecting consumers, while at the same time fostering innovation and competition.
-
Guiding principle 3: Financial and ICT infrastructures: Robust, safe, efficient and widely reachable financial and ICT infrastructures are effective for the provision of transaction accounts services, and also support the provision of broader financial services.
-
Guiding principle 4: Transaction account and payment product design: The transaction account and payment product offerings effectively meet a broad range of transaction needs of the target population, at little or no cost.
-
Guiding principle 5: Readily available access points: The usefulness of transaction accounts is augmented with a broad network of access points that also achieves wide geographical coverage, and by offering a variety of interoperable access channels.
-
Guiding principle 6: Awareness and financial literacy: Individuals gain knowledge, through awareness and financial literacy efforts, of the benefits of adopting transaction accounts, how to use those accounts effectively for payment and store-of-value purposes, and how to access other financial services.
-
Guiding principle 7: Large-volume, recurrent payment streams: Large-volume and recurrent payment streams, including remittances, are leveraged to advance financial inclusion objectives, namely by increasing the number of transaction accounts and stimulating the frequent usage of these accounts.
The CPMI and the World Bank Group believe that the guidance developed in this report will be essential to helping central banks and other stakeholders achieve effective financial access and broader financial inclusion. Given that safe, efficient and accessible retail payment systems and services are critical for greater financial inclusion, the report will be instrumental in supporting the goal of achieving Universal Financial Access by 2020.
The CPMI promotes the safety and efficiency of payment, clearing, settlement and related arrangements, thereby supporting financial stability and the wider economy. It is a global standard setter in this area. The CPMI monitors and analyses developments in these arrangements, both within and across jurisdictions. It aims to strengthen regulation, policy and practices regarding such arrangements worldwide. It also serves as a forum for central bank cooperation in related oversight, policy and operational matters, including the provision of central bank services.
Payment Aspects of Financial Inclusion (PAFI)
Having efficient, accessible and safe retail payment systems and services is necessary to be able to extend access to transaction accounts for the 2 billion worldwide people who are still unserved by regulated financial service providers.
The World Bank Group and the Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures (CPMI) of the Bank for International Settlements convened a task force on Payment Aspects of Financial Inclusion (PAFI) to comprehensively examine how payment systems and services affect financial inclusion efforts.
The PAFI task force, convened in 2014, brought together experts from central banks, development banks and international organizations to examine this issue in a comprehensive manner.
Its mandate was to examine demand- and supply-side factors affecting financial inclusion in the context of payment systems and services, and to suggest what measures could be taken to address these issues. The demand side is comprised by payment service users, like consumers, businesses, and government agencies and the supply side are payment service providers, like banks and authorized and/or regulated non-banks, as well as payment system operators.
The task force’s objectives were to:
-
Support the efforts of authorities to expand access to transaction accounts and the use of electronic payment services
-
Contribute to the recognition that safe and efficient payment services are important for the well-being of individuals, households and businesses, as well as a gateway to a broader range of financial services
-
Advance market efficiency, flexibility, integrity and competitiveness to support financial inclusion and stability
-
Facilitate the establishment of a balanced and proportional regulatory environment to facilitate effective, reliable, safe and cost-efficient access to payment services.
The PAFI work is essential to worldwide financial inclusion efforts, particularly to the World Bank Group’s UFA2020 initiative, whose goal is ensure that all working-age individuals and businesses can have access to at least one transaction account operated by an authorized and/or regulated payment service provider to:
-
Perform most, if not all, of their payment needs
-
Safely store some value
-
Serve as a gateway to other financial services
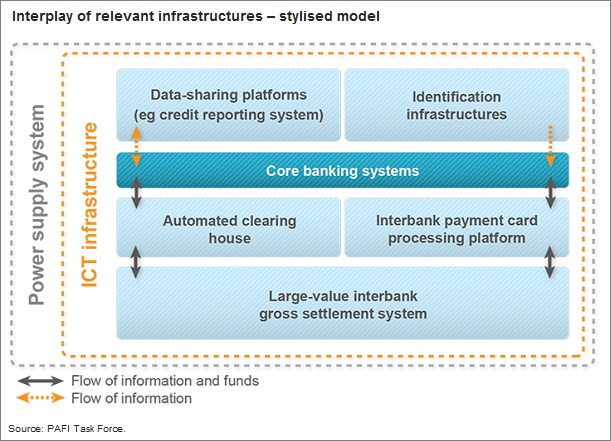
The task force found that certain financial and other relevant infrastructures are necessary for an efficient national payment system also form one of the basic foundations for financial inclusion. They include:
-
A large-value interbank settlement system
-
An interbank system for retail payments, in specific electronic funds transfers
-
A payment card processing platform or platforms and
-
An effective and efficient identification infrastructure
-
Credit reporting and other data-sharing platforms also play an important role
-
Finally, all a robust communications infrastructure and power supply system are essential.
Without these financial infrastructures, the efficient provision of various transaction accounts and electronic would be very difficult.
Public and private sector commitment, legal and regulatory framework, and financial and ICT infrastructures are the basic foundation that countries need to have in place to be able to expand access to transaction accounts. Designing useful payment and transaction accounts products which are made available through widespread access points, coupled with awareness and financial literacy efforts to inform and educate people on how to select and use them, as well as accelerating adoption of transaction accounts by shifting large volume use cases like wage or social benefit payments into those accounts constitute key elements that will make universal access to and frequent usage of transaction accounts possible.